The Magic of 3D printing
3D printing has revolutionized creation and manufacturing by turning digital designs into physical objects layer by layer. It allows for rapid prototyping and small-batch production, making it ideal for industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. Customization is a key strength, enabling unique solutions such as prosthetics, architectural models, and even edible prints. The technology has also sparked innovation in everyday life, allowing hobbyists and entrepreneurs to create personalized products. As 3D printing evolves, its potential continues to expand, reshaping how we innovate and bring ideas to life.
We offer 3D printing services using various technologies to meet your delivery and quality expectations. Our specialized factories are equipped for each technology, ensuring fast lead times to fulfill your customers’ needs. Here are the four different 3D printing technologies available to you.
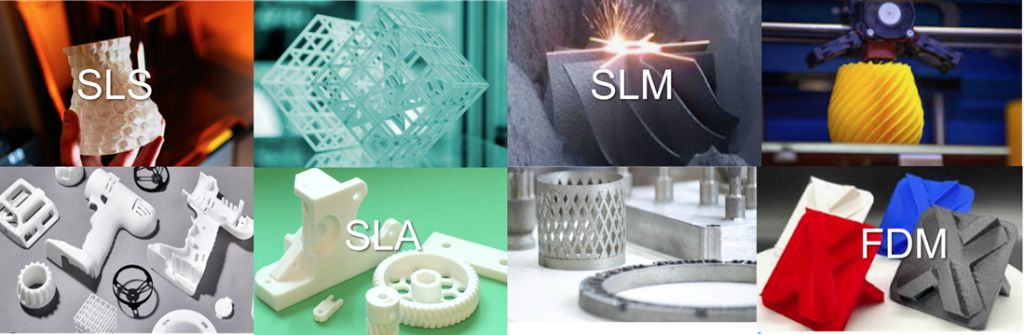
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a 3D printing technology in the powder bed fusion category, where a laser fuses thin layers of polymer powder to build a part. It primarily uses thermoplastic polymers, with Polyamide 12 (PA12 or Nylon 12) being the most common due to its strength, flexibility, lightweight, and resistance to various factors like impact, chemicals, heat, UV light, water, and dirt. Other materials used in SLS include PA11, nylon composites, polypropylene, and TPU.
Stereolithography (SLA) is a 3D printing technique that uses UV lasers to cure liquid polymer resin layer by layer. The process employs photosensitive thermoset polymers. Similar methods, such as Digital Light Processing (DLP) and Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), also use selective layer curing. After printing, parts undergo post-curing to improve their strength and stability.
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is an advanced 3D printing method that employs a high-powered laser to fully melt and fuse metallic powder layers, producing solid metal parts without the need for binders or fluxing agents. This technique ensures complete material melting, resulting in high-density and durable components. Metals commonly used in SLM include tungsten, nickel alloys, steel, aluminum, titanium, and copper, making it well-suited for applications demanding strength, precision, and reliability.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is an additive manufacturing process that uses material extrusion technology. It builds parts layer by layer by selectively depositing melted thermoplastic material along a predetermined path. The process uses filament reels made from thermoplastic polymers to create the final object. Common materials include PLA, ABS, PET, Nylon, TPU (flexible), and PC. The material choice depends on specific application needs, considering factors like ease of printing, maximum stress, elongation, impact resistance, layer adhesion, heat resistance, and the maximum temperature the object can handle before softening or deforming.
